Parallel Arrays C++ Example
Parallel array in C. Ask Question Asked 6 years, 4 months ago. Active 4 years, 11 months ago. Viewed 6k times 0. I have an assignment where we need to have 2 parallel arrays one is a list of city names and the other is sales amounts. There are only 8 cities to choose from. 2 parallel arrays must be used, initialized as follows: City. In this tutorial, I show you more about using Arrays in C. In the last tutorial, I've shown you some very basics of how arrays work, here I show you how to work with Parallel Arrays, also known as multiple arrays. Here You calculate and output results very easily. Arrays are very helpful.
Back to: C#.NET Tutorials For Beginners and Professionals
Parallel For in C# with Examples
In this article, I am going to discuss the static Parallel For in C# with some examples. Please read our previous article before proceeding to this article where we discussed the basics of Parallel Programming in C#. As part of this article, we will discuss the need and use of Parallel For loop comparing with the C# for loop. So, let’s start the discussion with one of the most frequently asked interview questions.
What is the difference between the Parallel For loop and standard C# for loop?
The main difference between the Parallel For loop and the standard C# for loop are as follows
Note1: When the iterations are independent of each other, means, subsequent iterations do not read the state updates made by previous iterations, then on such cases, we need to use Task Parallel Library (TPL) to run each iteration in parallel on all the available cores.
Note2: Moreover, the iteration should be an expensive iteration otherwise we will get negative performance, that we will also discuss as part of this article.
Syntax:
Let us see an example for a better understanding of the above two types of for loop in C#:
As you can see in the above example, the static “For” method of the static “Parallel” class is defined as public static ParallelLoopResult For(int fromInclusive, int toExclusive, Action<int> body);. Here the first parameter (i.e. int fromInclusive) is the start index. The second parameter (i.e. int toExclusive) is the end index and the third parameter (i.e. Action<int> body) is the delegate which is invoked once per iteration. You can find many overloaded versions of this method in the Parallel class.
Once you run the above code, you will get the following output.
As you can see in the above output, the standard C# for loop iterates sequentially using a single thread as a result, the results are printed sequentially. On the other hand, you can see with the Parallel for loop the results are not printed in sequential order. This is because it uses multiple threads to iterate over the collection. You can see that there are in our example it uses five threads to execute the code. It may vary in your system.
Let’s consider another example for the better understanding from a performance point of view.
First, we will write the example using C# for loop and will see how much time it will take to complete the execution. Then we will write the same example using Parallel For method and will see how much time it will take to complete the execution.
In the below example, we create a sequential loop. The loop iterates ten times, and the loop control variable increasing from zero to nine. In each iteration, the DoSomeIndependentTask method is called. The DoSomeIndependentTask method performs a calculation that is included to generate a long enough pause to see the performance improvement of the parallel version.
OUTPUT:
As you can see from the above output screen the for loop statement took approximately 3635 milliseconds to complete the execution.
Let’s rewrite the same example using the Parallel For method.
OUTPUT:
As shown in the above output image, the Parallel For method took 2357 milliseconds to complete the execution.
ParallelOptions class
The ParallelOptions class is one of the most useful class when working with multithreading. This class provides options to limit the number of concurrently executing loop methods.
The Degree of parallelism:
Using the Degree of parallelism we can specify the maximum number of threads to be used to execute the program. Following is the syntax to use ParallelOptions class with Degree of parallelism.
The MaxDegreeOfParallelism property affects the number of concurrent operations run by Parallel method calls that are passed this ParallelOptions instance. A positive property value limits the number of concurrent operations to the set value. If it is -1, there is no limit on the number of concurrently running operations.
Let us see an example for better an understanding of the MaxDegreeOfParallelism.
OUTPUT:
As we set the degree of parallelism to 2. So, a maximum of 2 threads is used to execute the code that we can see from the above output.
Terminating a Parallel Loop:
The below example shows how to break out of a For loop and also how to stop a loop. In this context, “break” means complete all iterations on all threads that are prior to the current iteration on the current thread, and then exit the loop. “Stop” means to stop all iterations as soon as convenient.
In a Parallel.For or Parallel.ForEach loop, you cannot use the same break or Exit statement that is used in a sequential loop because those language constructs are valid for loops, and a parallel “loop” is actually a method, not a loop. Instead, you use either the Stop or Break method.
In the next article, I am going to discuss theParallel ForEach Method in C#with some examples. Here, In this article, I try to explain the Parallel For in C# with some examples. I hope you understood the need and use of Parallel For method in C#.
Please have a look at our LINQ Tutorials.
This article is part of our on-going C programming series.
There are times while writing C code, you may want to store multiple items of same type as contiguous bytes in memory so that searching and sorting of items becomes easy. For example:
- Storing a string that contains series of characters. Like storing a name in memory.
- Storing multiple strings. Like storing multiple names.
C programming language provides the concept of arrays to help you with these scenarios.
1. What is an Array?
An array is a collection of same type of elements which are sheltered under a common name.
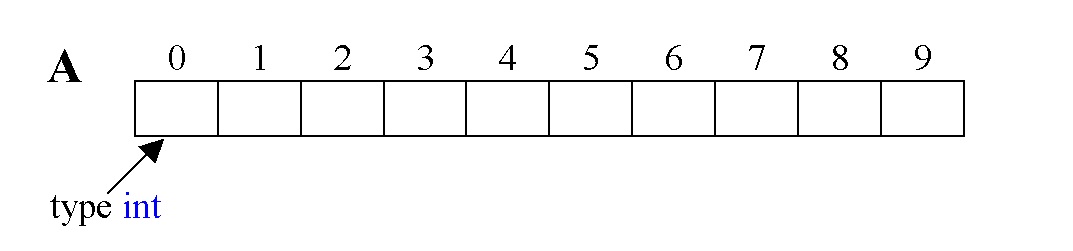
An array can be visualised as a row in a table, whose each successive block can be thought of as memory bytes containing one element. Look at the figure below :
An Array of four elements:
The number of 8 bit bytes that each element occupies depends on the type of array. If type of array is ‘char’ then it means the array stores character elements. Since each character occupies one byte so elements of a character array occupy one byte each.
2. How to Define an Array?
An array is defined as following :
- type-of-array: It is the type of elements that an array stores. If array stores character elements then type of array is ‘char’. If array stores integer elements then type of array is ‘int’. Besides these native types, if type of elements in array is structure objects then type of array becomes the structure.
- name-of-array: This is the name that is given to array. It can be any string but it is usually suggested that some can of standard should be followed while naming arrays. At least the name should be in context with what is being stored in the array.
- [number of elements]: This value in subscripts [] indicates the number of elements the array stores.
For example, an array of five characters can be defined as :
3. How to Initialize an Array?
An array can be initialized in many ways as shown in the code-snippets below.
Initializing each element separately. For example :
Initializing array at the time of declaration. For example :
In the above example an array of five integers is declared. Note that since we are initializing at the time of declaration so there is no need to mention any value in the subscripts []. The size will automatically be calculated from the number of values. In this case, the size will be 5.
Parallel Arrays Python
Initializing array with a string (Method 1):
Strings in C language are nothing but a series of characters followed by a null byte. So to store a string, we need an array of characters followed by a null byte. This makes the initialization of strings a bit different. Let us take a look :
Since strings are nothing but a series of characters so the array containing a string will be containing characters
In the above declaration/initialization, we have initialized array with a series of character followed by a ‘0’ (null) byte. The null byte is required as a terminating byte when string is read as a whole.
Initializing array with a string (Method 2):
Here we neither require to explicitly wrap single quotes around each character nor write a null character. The double quotes do the trick for us.
4. Accessing Values in an Array
Now we know how to declare and initialize an array. Lets understand, how to access array elements. An array element is accessed as :
As we can see above, the 6th element of array is accessed as ‘arr[5]’.
Note that for an array declared as int arr[5]. The five values are represented as: arr[0] arr[1] arr[2] arr[3] arr[4] and not arr[1] arr[2] arr[3] arr[4] arr[5]
The first element of array always has a subscript of ‘0’
5. Array of Structures
The following program gives a brief idea of how to declare, initialize and use array of structures.
The output of the above program comes out to be :
6. Array of Char Pointers
The following program gives a brief Idea of how to declare an array of char pointers :
The output of the above program is :
7. Pointer to Arrays
Pointers in C Programming language is very powerful. Combining pointers with arrays can be very helpful in certain situations.
As to any kind of data type, we can have pointers to arrays also. A pointer to array is declared as :
For example :
The above example declares a pointer ptr to an array of 5 integers.
Lets look at a small program for demonstrating this :
In the above program, we declared and initialized an array ‘arr’ and then declared a pointer ‘ptr’ to an array of 3 characters. Then we initialized ptr with the address of array ‘arr’.
8. Static vs Dynamic Arrays
Static arrays are the ones that reside on stack. Like :
Dynamic arrays is a popular name given to a series of bytes allocated on heap. this is achieved through malloc() function. Like :
The above line allocates a memory of 10 bytes on heap and we have taken the starting address of this series of bytes in a character pointer ptr.
Static arrays are used when we know the amount of bytes in array at compile time while the dynamic array is used where we come to know about the size on run time.
9. Decomposing Array into Pointers
Internally, arrays aren’t treated specially, they are decomposed into pointers and operated there-on. For example an array like :
When accessed like :
is decomposed as :
So we see above that the same old pointers techniques are used while accessing array elements.
10. Character Arrays and Strings
Mostly new programmers get confused between character arrays and strings. Well, there is a very thin line between the two. This thin line only comprises of a null character ‘0’ . If this is present after a series of characters in an array, then that array becomes a string.
This is an array:
This is a string:
Note : A string can be printed through %s format specifier in printf() while an printing an array through %s specifier in printf() is a wrong practice.
11. Bi-dimensional and Multi-dimensional Arrays
The type of array we discussed until now is single dimensional arrays. As we see earlier, we can store a set of characters or a string in a single dimensional array. What if we want to store multiple strings in an array. Well, that wont be possible using single dimensional arrays. We need to use bi-dimensional arrays in this case. Something like :
The above declaration can be thought of as 5 rows and 10 columns. Where each row may contain a different name and columns may limit the number of characters in the name. So we can store 5 different names with max length of 10 characters each.
Similarly, what if we want to store different names and their corresponding addresses also. Well this requirement cannot be catered even by bi-dimensional arrays. In this case we need tri-dimensional (or multi-dimensional in general) arrays. So we need something like :
So we can have 5 names with max capacity of 10 characters for names and 50 characters for corresponding addresses.
Since this is an advanced topic, So we won’t go into practical details here.

12. A Simple C Program using Arrays
Consider this simple program that copies a string into an array and then changes one of its characters :
I think the program is self explanatory as I have added plenty of comments. The output of the above program is :
So we see that we successfully copied the string into array and then changed the first character in the array.
13. No Array Bound Check in a C Program
What is array bound check? Well this is the check for boundaries of array declared. For example :
The above array ‘arr’ consumes 5 bytes on stack and through code we can access these bytes using :
Now, C provides open power to the programmer to write any index value in [] of an array. This is where we say that no array bound check is there in C. SO, misusing this power, we can access arr[-1] and also arr[6] or any other illegal location. Since these bytes are on stack, so by doing this we end up messing with other variables on stack. Consider the following example :
In the above example, we have declared an array of 3 integers but try to access the location arr[3] (which is illegal but doable in C) and change the value kept there.
But, we end up messing with the value of variable ‘b’. Cant believe it?, check the following output . We see that value of b changes from 10 to 12.
If you enjoyed this article, you might also like..
Next post: 6 Linux Crontab Command Examples
C++ Parallel Sort
Previous post: Top 25 Best Linux Performance Monitoring and Debugging Tools